- Kerberos Event Id
- Scom Alert No Key To Generate Kerberos Ticket
- No Key To Generate Kerberos Ticket Resolution State
- No Key To Generate Kerberos Ticket Online
Applies to
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
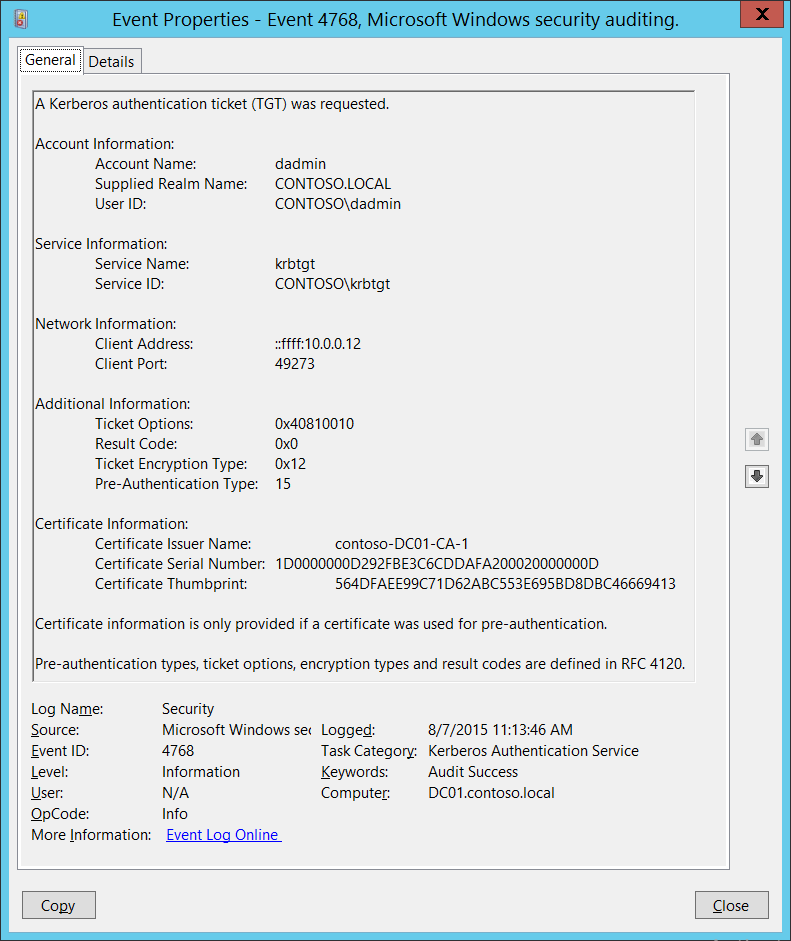
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Client requests an authentication ticket (TGT) from the Key Distribution Center (KDC). There are no real contenders to replace Kerberos in the pipeline. Most of the advancements in security are to protect your password or provide a different method of validating who you are to Kerberos. The issue is I want to be able to generate a Kerberos ticket upon logging in, or at least so I don't have to enter my password in, at all. I used GSSAPI auth to get to localhost, so I got in with a kerberos ticket. Can I pass that one along, perhaps? I suspect this is your problem, actually. The only non-obvious step here would be that there is a PAM module on S1 that used your credentials to perform a kinit and gets you a ticket granting ticket from K (client authentication). Then, when you SSH to S2 using Kerberos authentication, an client service authentication takes place. I am working on a web based application and my application supports SSO (We use Kerberos protocol. The Active Directory mapping and SPN configurations are all done). We are using GWT 2.4 for the GUI part and we support standalone and SSO modes for the application (We can switch between these modes using a utility). This event generates every time Key Distribution Center issues a Kerberos Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT). This event generates only on domain controllers. If TGT issue fails then you will see Failure event with Result Code field not equal to “ 0x0 ”. Normally, Kerberos would be integrated with PAM pamkrb5.so. It will attempt to acquire a Kerberos ticket based on your username and the password you supply. It can also use that to verify whether you are allowed to login, but that can be set to ignore if you just want the ticket.
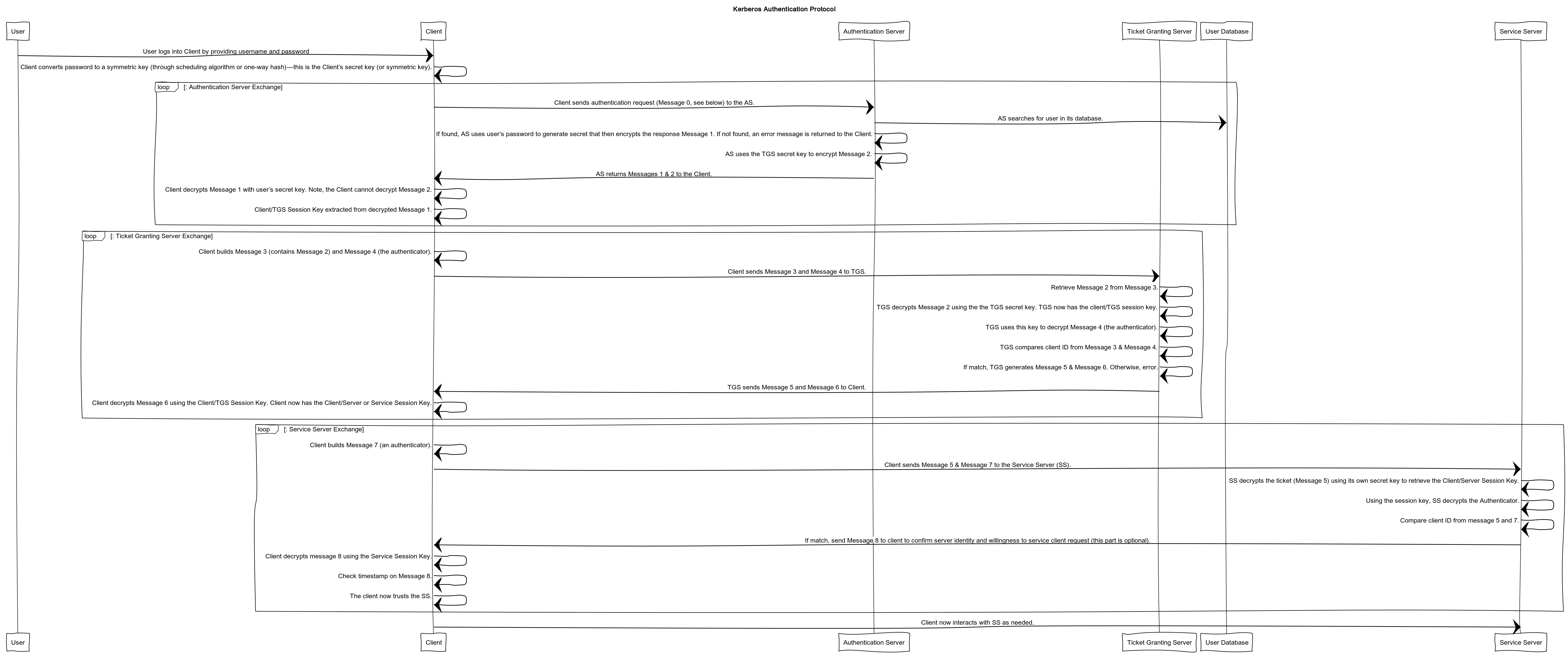
Audit Kerberos Authentication Service determines whether to generate audit events for Kerberos authentication ticket-granting ticket (TGT) requests.
If you configure this policy setting, an audit event is generated after a Kerberos authentication TGT request. Success audits record successful attempts and Failure audits record unsuccessful attempts.
Event volume: High on Kerberos Key Distribution Center servers.
This subcategory contains events about issued TGTs and failed TGT requests. It also contains events about failed Pre-Authentications, due to wrong user password or when the user’s password has expired.
| Computer Type | General Success | General Failure | Stronger Success | Stronger Failure | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domain Controller | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | We recommend Success auditing, because you will see all Kerberos Authentication requests (TGT requests), which are a part of domain account logons. Also, you can see the IP address from which this account requested a TGT, when TGT was requested, which encryption type was used and so on. We recommend Failure auditing, because you will see all failed requests with wrong password, username, revoked certificate, and so on. You will also be able to detect Kerberos issues or possible attack attempts. Expected volume is high on domain controllers. |
| Member Server | No | No | No | No | This subcategory makes sense only on domain controllers. |
| Workstation | No | No | No | No | This subcategory makes sense only on domain controllers. |
Events List:
4768(S, F): A Kerberos authentication ticket (TGT) was requested.
4771(F): Kerberos pre-authentication failed.
4772(F): A Kerberos authentication ticket request failed.
 -->
-->Displays a list of currently cached Kerberos tickets. This information applies to Windows Server 2012. For examples of how this command can be used, see Examples.
Kerberos Event Id
Syntax
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| -lh | Denotes the high part of the user's locally unique identifier (LUID), expressed in hexadecimal. If neither –lh or –li are present, the command defaults to the LUID of the user who is currently signed in. |
| -li | Denotes the low part of the user's locally unique identifier (LUID), expressed in hexadecimal. If neither –lh or –li are present, the command defaults to the LUID of the user who is currently signed in. |
| tickets | Lists the currently cached ticket-granting-tickets (TGTs), and service tickets of the specified logon session. This is the default option. |
| tgt | Displays the initial Kerberos TGT. |
| purge | Allows you to delete all the tickets of the specified logon session. |
| sessions | Displays a list of logon sessions on this computer. |
| kcd_cache | Displays the Kerberos constrained delegation cache information. |
| get | Allows you to request a ticket to the target computer specified by the service principal name (SPN). |
| add_bind | Allows you to specify a preferred domain controller for Kerberos authentication. |
| query_bind | Displays a list of cached preferred domain controllers for each domain that Kerberos has contacted. |
| purge_bind | Removes the cached preferred domain controllers for the domains specified. |
| kdcoptions | Displays the Key Distribution Center (KDC) options specified in RFC 4120. |
| /? | Displays Help for this command. |
Remarks
Membership in Domain Admins, or equivalent, is the minimum required to run all the parameters of this command.
If no parameters are provided, Klist will retrieve all the tickets for the currently logged on user.
The parameters display the following information:
tickets
Lists the currently cached tickets of services that you have authenticated to since logon. Displays the following attributes of all cached tickets:
- LogonID: The LUID
- Client: The concatenation of the client name and the domain name of the client
- Server: The concatenation of the service name and the domain name of the service
- KerbTicket Encryption Type: The encryption type that is used to encrypt the Kerberos ticket
- Ticket Flags: The Kerberos ticket flags
- Start Time: The time from which the ticket will be valid
- End Time: The time the ticket becomes no longer valid. When a ticket is past this time, it can no longer be used to authenticate to a service or be used for renewal
- Renew Time: The time that a new initial authentication is required
- Session Key Type: The encryption algorithm that is used for the session key
tgt
Lists the initial Kerberos TGT and the following attributes of the currently cached ticket:
- LogonID: Identified in hexadecimal
- ServiceName: krbtgt
- TargetName <SPN>: krbtgt
- DomainName: Name of the domain that issues the TGT
- TargetDomainName: Domain that the TGT is issued to
- AltTargetDomainName: Domain that the TGT is issued to
- Ticket Flags: Address and target actions and type
- Session Key: Key length and encryption algorithm
- StartTime: Local computer time that the ticket was requested
- EndTime: Time the ticket becomes no longer valid. When a ticket is past this time, it can no longer be used to authenticate to a service.
- RenewUntil: Deadline for ticket renewal
- TimeSkew: Time difference with the Key Distribution Center (KDC)
- EncodedTicket: Encoded ticket
purge
Allows you to delete a specific ticket. Purging tickets destroys all tickets that you have cached, so use this attribute with caution. It might stop you from being able to authenticate to resources. If this happens, you will have to log off and log on again.
- LogonID: Identified in hexadecimal
sessions
Allows you to list and display the information for all logon sessions on this computer.
- LogonID: If specified, displays the logon session only by the given value. If not specified, displays all the logon sessions on this computer.
kcd_cache/dll-files-fixer-licence-key-generator.html.
Allows you to display the Kerberos constrained delegation cache information.
- LogonID: If specified, displays the cache information for the logon session by the given value. If not specified, displays the cache information for the current user's logon session.
get
Allows you to request a ticket to the target that is specified by the SPN.
- LogonID: If specified, requests a ticket by using the logon session by the given value. If not specified, requests a ticket by using the current user's logon session.
- kdcoptions: Requests a ticket with the given KDC options
add_bind
Allows you to specify a preferred domain controller for Kerberos authentication.
query_bind
Allows you to display cached, preferred domain controllers for the domains.
purge_bind
inventory control software free for mac Allows you to remove cached, preferred domain controllers for the domains.
kdcoptions
For the current list of options and their explanations, see RFC 4120.
Other considerations
- Klist.exe is available in Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8, and it requires no special installation.
Scom Alert No Key To Generate Kerberos Ticket
Examples
No Key To Generate Kerberos Ticket Resolution State
- When you are diagnosing an Event ID 27 while processing a ticket-granting service (TGS) request for the target server, the account did not have a suitable key to generate a Kerberos ticket. You can use Klist to query the Kerberos ticket cache to determine if any tickets are missing, if the target server or account is in error, or if the encryption type is not supported.
- When you diagnose errors and you want to know the specifics of each ticket-granting-ticket that is cached on the computer for a logon session, you can use Klist to display the TGT information.
- If you are unable to establish a connection and diagnosis might take too long, you can purge the Kerberos ticket cache, log off, and then log back on.
- When you want to diagnose a logon session for a user or a service, you can use the following command to find the LogonID that is used in other Klist commands.
- When you want to diagnose Kerberos constrained delegation failure, you can use the following command to find the last error that was encountered.
- When you want to diagnose if a user or a service can get a ticket to a server, you can use this command to request a ticket for a specific SPN.
- When diagnosing replication issues across domain controllers, you typically need the client computer to target a specific domain controller. In these cases, you can use the following command to target the client computer to that specific domain controller.
- To query what domain controllers this computer recently contacted, you can use the following command.
- When you want Kerberos to rediscover domain controllers, you can use the following command. This command can also be used to flush the cache before creating new domain controller bindings with klist add_bind.